Hot from the press: Two more published papers!
We congratulate two N&N researchers for two new publications: Marti Gich for his third publication within a very short period of time and Anna Roig who is a co-author of one of the two recent publications. Both studies have been done together with other ICMAB researchers and collaborators from other institutions.
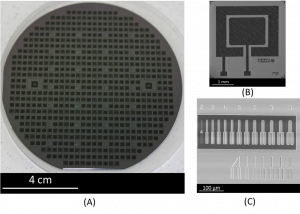
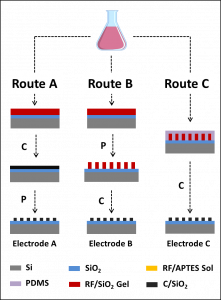
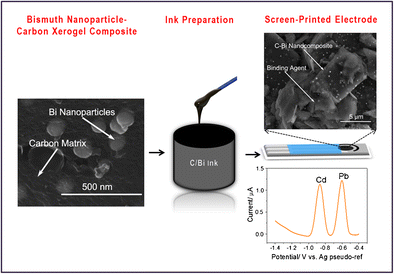
Title: Carbon–Silica Composites to Produce Highly Robust Thin-Film Electrochemical Microdevices
Authors: Pengfei Niu, Laura Asturias-Arribas, Xavier Jordà, Alejandro R. Goñi, Anna Roig, Martí Gich, César Fernández-Sánchez
Citation: Niu, P. et al. Carbon-Silica Composites to Produce Highly Robust Thin-Film Electrochemical Microdevices. Adv. Mater. Technol. 1700163 (2017).
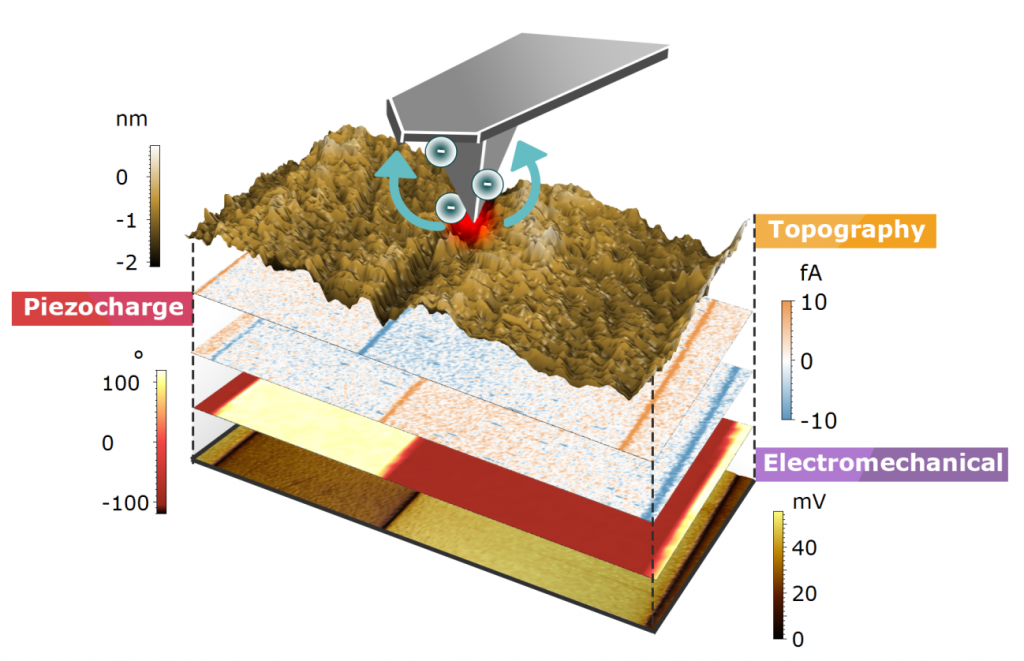
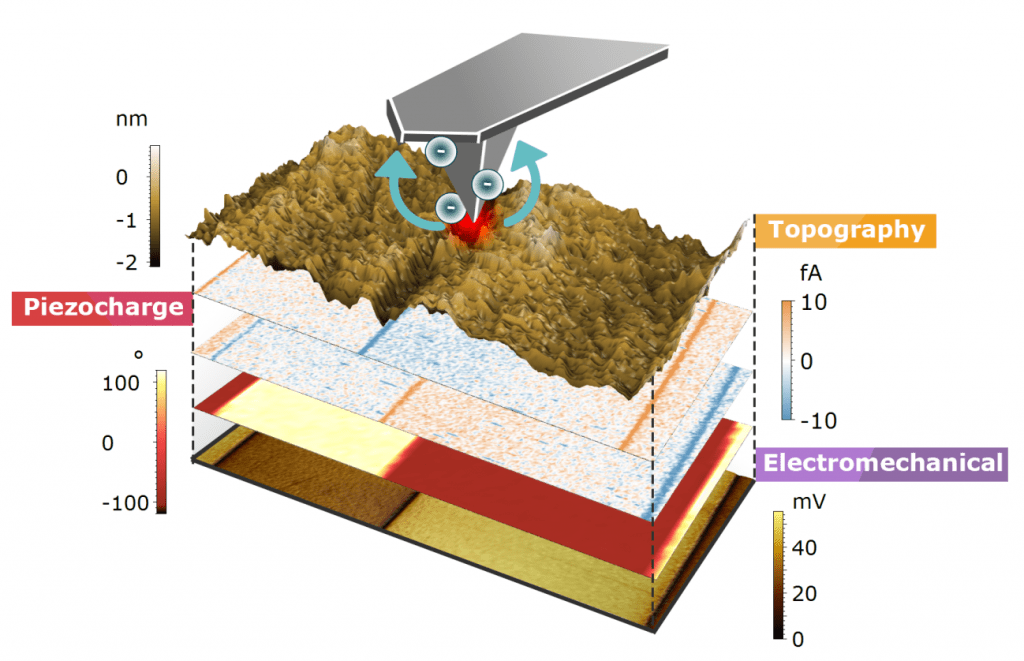
Title: Piezo-generated charge mapping revealed through direct piezoelectric force microscopy
Authors: A. Gomez, M. Gich, A. Carretero-Genevrier, T. Puig and X. Obradors
Citation: Gomez, A., Gich, M., Carretero-Genevrier, A., Puig, T. & Obradors, X. Piezo-generated charge mapping revealed through direct piezoelectric force microscopy. Nat. Commun. 8, 1113 (2017).
We strongly recommend to read the Peer Review File of this paper published in Nature communications where the exchange of opinions between the authors and the referees is shown.