Paper Accepted in ACS Biomaterials Science and Engineering
Protective effects of Bovine Serum Albumin on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles evaluated in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans
Laura Gonzalez-Moragas, Si-Ming Yu, Elisa Carenza, Anna Laromaine*, Anna Roig
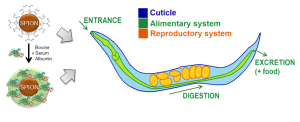
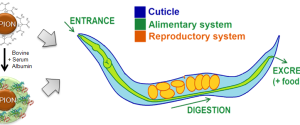
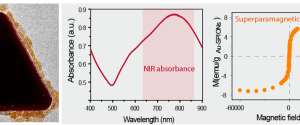
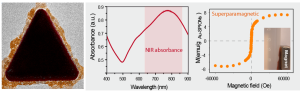
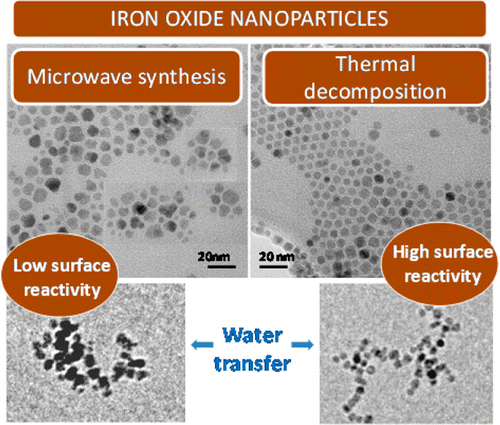
Nanomaterials have unique biological reactivity that need to be thoroughly investigated. In this context, the use of simple in vivo models to biologically evaluate nanoparticles is currently in increasing demand as they offer low-cost and information-rich experiments. In this work, we evaluated how surface modification (citrate and protein-coated) of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles induces changes in their toxicological profile and biodistribution using the animal model Caenorhabditis elegans and combining techniques from materials science and biochemistry.