HOT FROM THE PRESS
Rapid synthesis of water-dispersible superparamagnetic iron oxide
nanoparticles by a microwave-assisted route for safe labeling of
endothelial progenitor cells
Elisa Carenza, Verónica Barceló, Anna Morancho, Joan Montaner, Anna Rosell*, Anna Roig*
Acta-Biomaterialia 10 (2014) pp. 3775-3785) DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.04.01
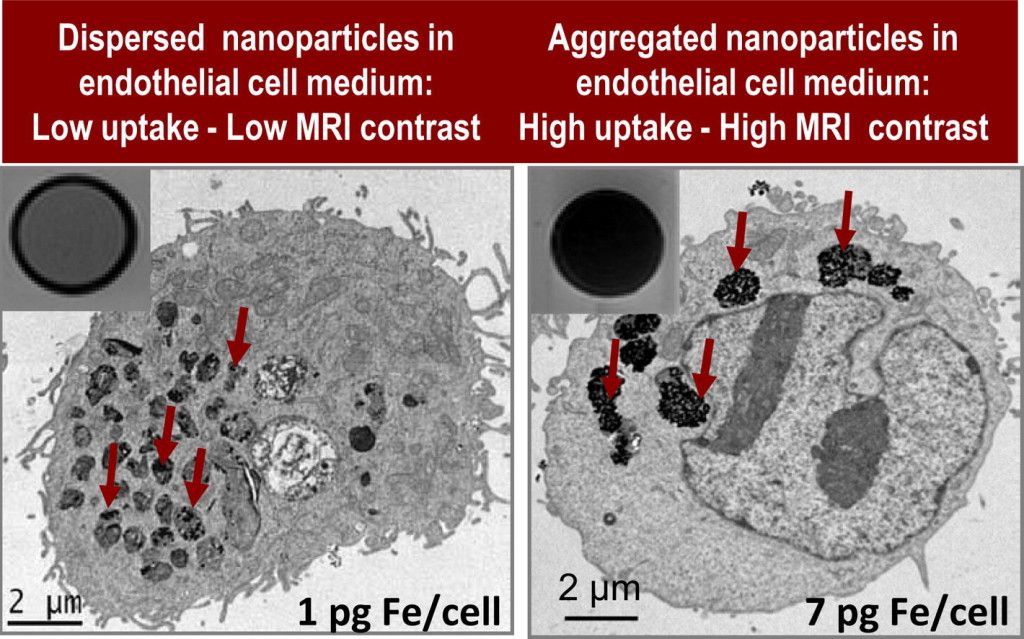
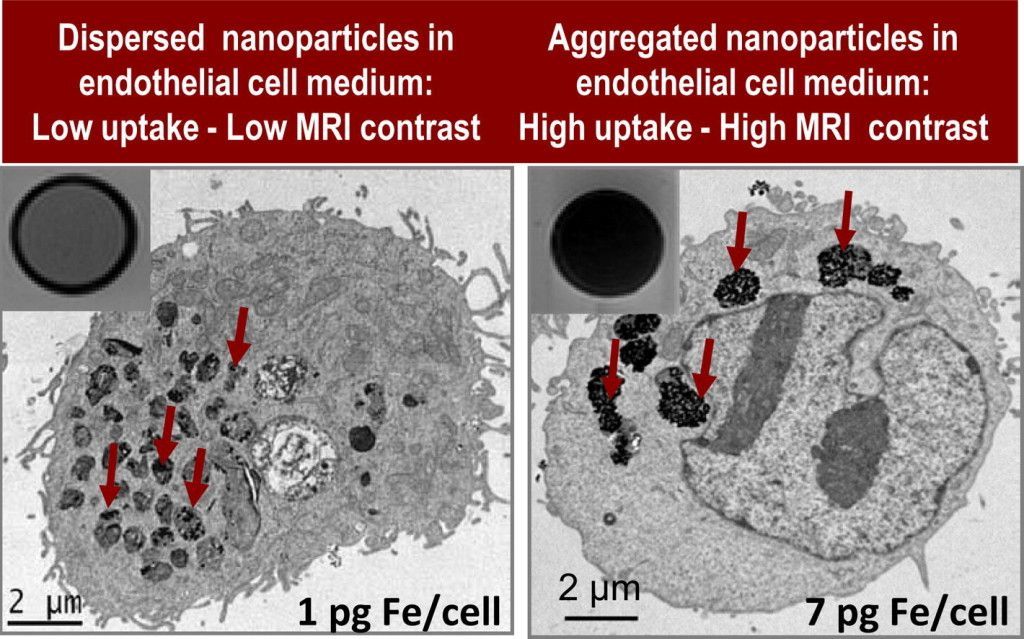
Highly crystalline citrate coated iron oxide superparamagnetic nanoparticles readily dispersible in water were fabricated by an extremely fast microwave-assisted route, the uptake of magnetic nanoparticles by endothelial cells is further investigated. Nanoparticles form large aggregates when added to complete endothelial cell media. The size of aggregates was controlled by adjusting the ionic strength of the media. The internalization of nanoparticles into endothelial cells was then investigated by transmission electron microscopy, magnetometry and chemical analysis together with cell viability assays. Interestingly, a seven-fold more efficient uptake was found for systems with larger nanoparticle aggregates which also showed significantly higher magnetic resonance imaging effectiveness without compromising cell viability and functionality. We are thus presenting an example of a straightforward microwave synthesis of citrate-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for safe endothelial progenitor cell labeling and good magnetic resonance cell imaging with potential application in magnetic cell guiding and in vivo cell tracking.

