
Hot off the press: accepted manuscript
 Enhanced stability of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in biological media using a pH adjusted-BSA adsorption protocol
Enhanced stability of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in biological media using a pH adjusted-BSA adsorption protocol
Si-Ming Yu • Anna Laromaine* • Anna Roig*
J Nanopart Res (2014) 16:2484, DOI 10.1007/s11051-014-2484-1
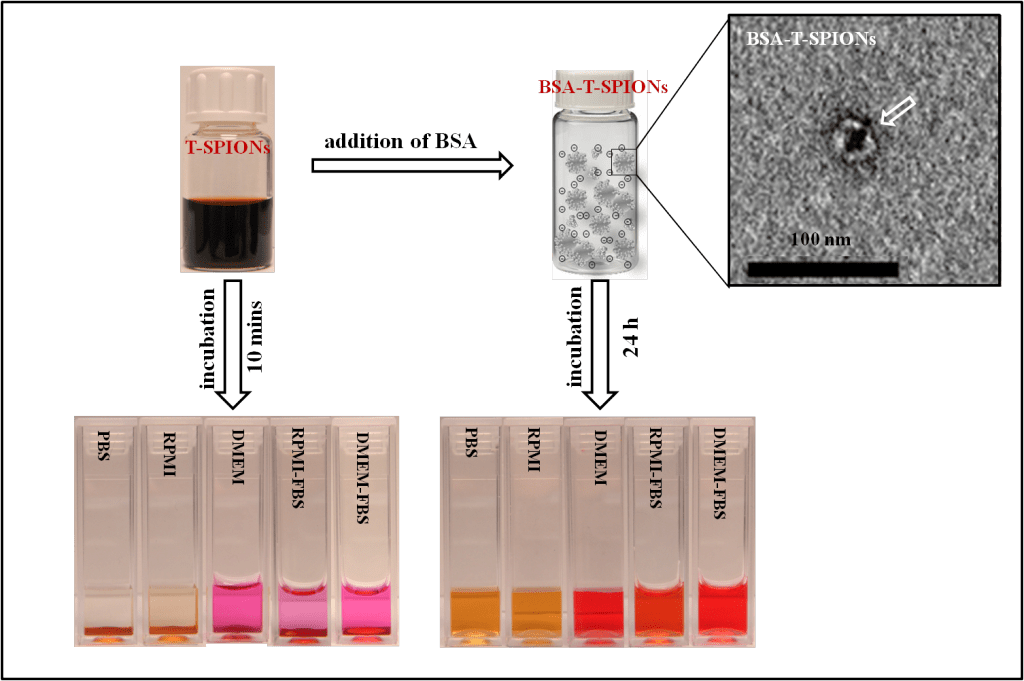
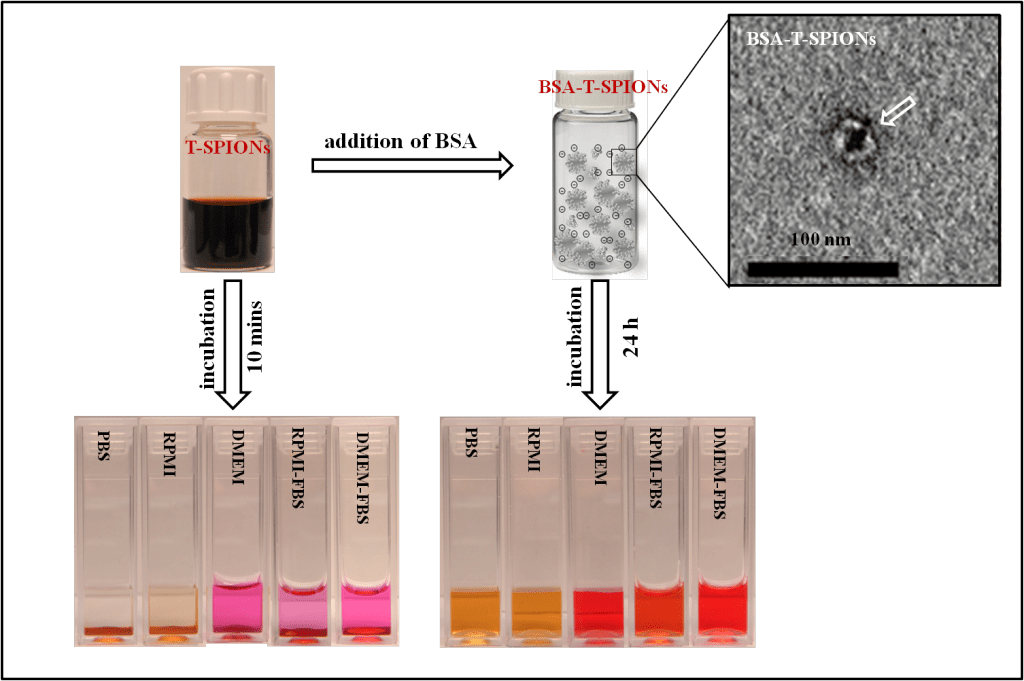
SPIONs were synthesized by a facile, rapid and cost effective microwave assisted method. Then, a modified pH adjusted-BSA adsorption protocol and an addition of excess trisodium citrate dihydrate (Na3Cit) were used to enhance their stability in the media. The BSA adsorption protocol showed great efficiency in stabilizing the dispersed state of both SPIONs in the tested media, while the addition of excess Na3Cit showed limit effect. The formed BSA layer on SPIONs could be imaged by negative staining TEM, and revealed by Cryo-TEM, FTIR, DLS and the zeta potential measurements. Results indicated that BSA forms a monolayer of a thickness of about 3 ± 1 nm and BSA interacts with SPIONs coating rather than by replacing them and interacting directly with the SPIONs surface. This synthetic method and stabilization protocol offer a general methodology to obtain SPIONs with a variety of surfactants, stable in different biological media in few minutes.

