Review article in nanomaterials for cardiac arrhytmia
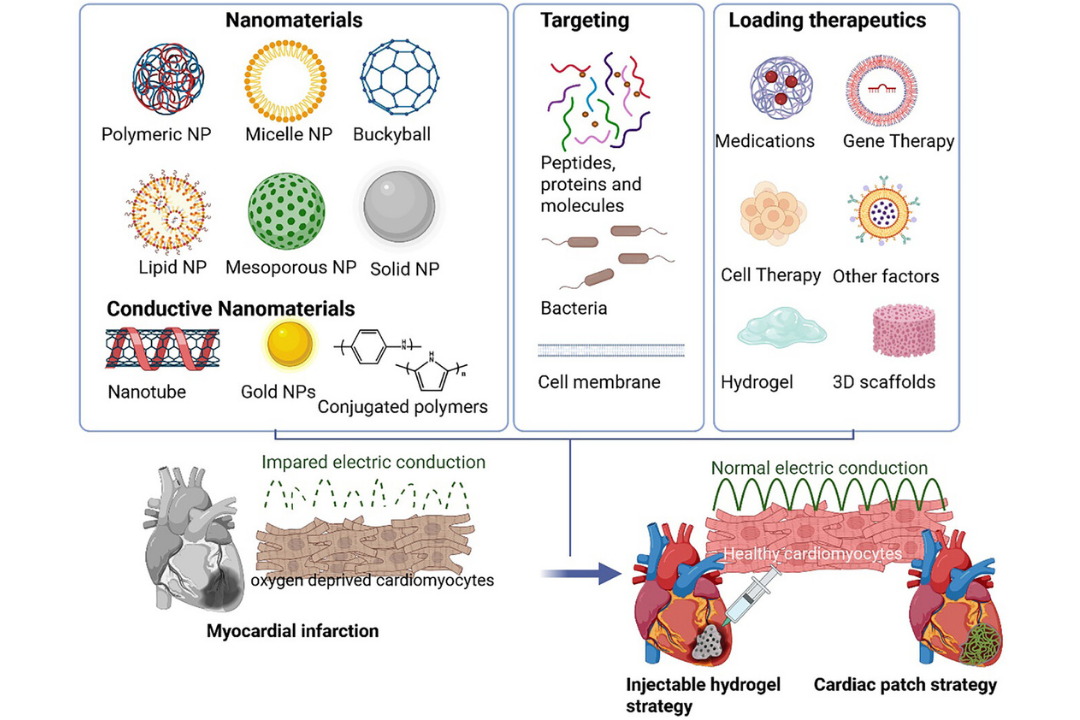
The NN researcher Anna Laromaine and the former NN PhD student Sumithra Y. Srinivasan published a review article in Advanced Healthcare Materials. The review addresses the development of nanomaterials that can mimic the properties of native cardiac tissue, as well as novel bioevaluation methodologies to evaluate them. Authors advocate for the use of small animals, such as C. elegans, to speed research and bridge the gap between in vitro studies and rodent models.
Read more …Review article in nanomaterials for cardiac arrhytmia
- Created on .
- Hits: 225